Inflammation of small joints most often does not develop on its own, but against the background of some general diseases. Finger arthritis is a characteristic symptom of rheumatoid arthritis, but it can also be one of the manifestations of some other disease. It is very important to seek medical help in a timely manner, identify the cause of the disease and start treatment to avoid serious complications and disabilities. In this article you will find all the information you need to know about this disease.
General information about the disease
Finger arthritis is inflammation of the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of the fingers. The disease occurs quite often, at any age. According to statistics, women are sicker with them after 40 years. This is explained by the fact that, compared to men, women have a greater load on their hands and fingers. Finger arthritis code of unspecified origin according to ICD-10 M13.
Depending on the cause that caused it, the disease can manifest itself only in the small joints of the fingers and can be combined with damage to the large joints. The onset of the disease can be acute, subacute and chronic, but then the course in most cases becomes protracted or chronic. The exception is post-traumatic arthritis of the fingers: with proper treatment, it ends in full recovery. But if the treatment was not prescribed in time, then it also takes a chronic course.
Causes of the inflammatory process in the joints of the fingers
The causes of the disease can be different. Most often, the small joints of the fingers are affected by rheumatoid arthritis - an autoimmune disease (with an allergy to the patient's tissues), which is based on a hereditary predisposition. The starting point for the onset of the disease is usually some type of infection. After that, after a while, genetically predisposed individuals develop arthritis of the fingers. In the future, other larger joints may be affected.
Another common cause of inflammation of the small joints of the hands is psoriatic arthritis. It is also a hereditary autoimmune disease, in which the joints of the fingertips (distal) are mainly affected, with a simultaneous characteristic lesion of the nails. This usually occurs against the background of the existing skin manifestations of psoriasis, but sometimes the symptoms of arthritis in the joints of the fingers appear first.
Quite often, arthritis of the joints of the fingers develops with gout. The disease has a metabolic (metabolic) origin: the exchange of uric acid salts is disturbed, they are deposited in the joint and periarticular tissues, causing an inflammatory process.
Post-traumatic arthritis of the finger joints is sometimes occupational in nature. It develops with a constant mild injury to the hands of jewelers, seamstresses, hairdressers, etc. The inflammatory process is constantly supported by further trauma and becomes chronic. After acute injuries (sports, household), acute arthritis can develop, which then disappears completely.
Other types of arthritis rarely cause damage to small joints. The provoking factors that contribute to the development of arthritis of the small joints of the hands are hormonal changes (adolescence, pregnancy, menopause), stress, frequent colds and allergic diseases, bad habits and professional activities.
Finger Arthritis Symptoms
Symptoms can be different, they depend on the nature of the course of the inflammatory process (acute, subacute, chronic), as well as on the clinical form of the underlying disease.
First signs
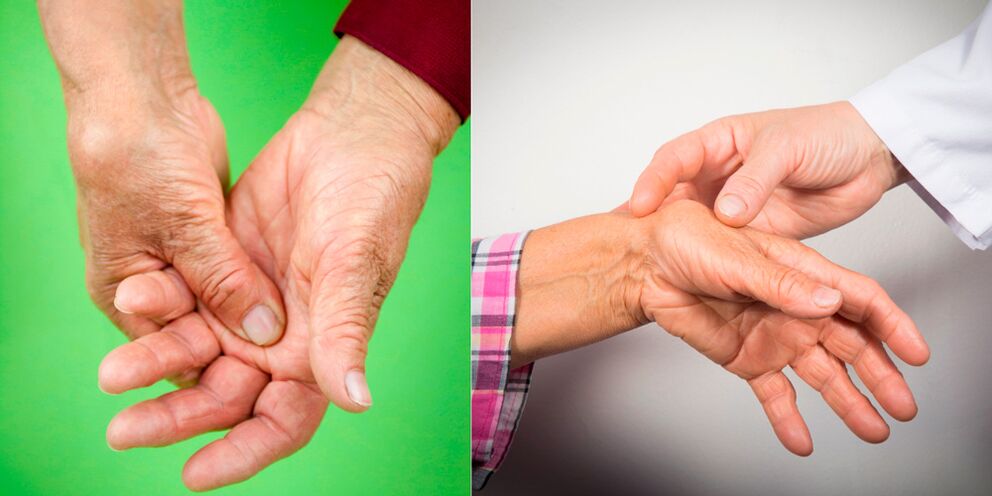
The onset of the disease is slow in most cases. There are aching pains in the hands and stiffness of movements in the morning. At first, such a symptom lasts on average no more than half an hour, and then passes. The pains are painful, constant, their intensity slowly increases.
Less often, the onset is acute. Pain appears in one or more small joints of the fingers, accompanied by redness and swelling of the surrounding tissue. The function of the joint is impaired - it is difficult to bend and stretch out, sometimes it is impossible to do so due to pain.
With an acute onset of the disease, the general condition of the patient often suffers: fever, malaise and headache appear. If the process develops subacute or chronic, there may be no general manifestations, changes in the affected joints may also not be very pronounced.
The most important thing to do when arthritis symptoms appear is to see a doctor. The earlier this happens, the more likely it is to stop the inflammatory process early on.
Obvious symptoms
Obvious signs of chronic arthritis of the hand include the appearance of edema and redness of the tissues around the affected areas of the hands, as well as the involvement of other joints in the pathological process on the same or other. The appearance of new foci of inflammation can be accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature, increased pain and dysfunction of the affected joints. But more often exacerbations of rheumatoids occur without general manifestations.
After a while, the inflammatory process can somewhat reduce its intensity, local inflammation and general symptoms subside. Subsequently, the process becomes chronic. Morning stiffness of movements appears, patients notice the feeling of tight gloves on the hand, which do not allow movement. Some time after getting up in the morning and starting physical activity, this sensation diminishes or even disappears. Also characteristic is the appearance of crepitus (friction and clicking) in the affected joint joints.
When the patient is not receiving treatment for arthritis, there is an alternation of exacerbations and remissions with constant pain and rapid formation of joint deformities (with rheumatoid arthritis) or fingertip fusion and shortening (with psoriatic arthritis). Arthritis of the thumb most often develops with gout, proceeds with severe pain, swelling, redness, then disappears without a trace, but with frequent relapses deformation and loss of joint function also develop.
Dangerous symptoms
Emergency medical care is needed for the following symptoms of finger arthritis:
- elevated body temperature (38 - 39 °) for 5 or more days;
- a sharp rise in temperature, increased inflammation and pain in the joint with an already existing inflammatory process - may indicate the onset of suppuration;
- involvement in the pathological process of new small or large joints;
- the appearance of blackened tissue on the fingertips (necrosis) in psoriatic arthritis.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What is the danger of the disease
The main danger of any type of chronic arthritis is in the progression of the inflammatory process, which eventually turns into degenerative-dystrophic with deformity and disability of the limbs. The longer the arthritis lasts, the greater the risk of complications.
Stages of the disease
Arthritis of the joints of the fingers has 4 stages of development, depending on the degree of joint damage, detected during the instrumental examination:
- Initial state.In the presence of severe or minor clinical signs of inflammation on the x-ray, you may see signs of inflammation in the form of expansion of the joint space. On ultrasound, you can see the presence of an increase in the volume of joint fluid. Symptoms can be pronounced or almost absent in the chronic course of the disease.
- Progressive inflammation.On X-rays and ultrasounds, the signs of inflammation are clearly visible. Articular cartilage is destroyed, in their place a loose connective tissue is formed - cloth. The process takes on a wavy (exacerbation-remission) or constantly progressive course. Pain and stiffness increase.
- ankylosis of connective tissue.The connective tissue of the cloth becomes rough, grows and connects the bony surfaces that form the joints, as a result of which movement in the joint is limited. The fingers are deformed.
- bone ankylosis.Instead of connective tissue, bone tissue grows in the joint, which leads to complete immobility of the joint and the loss of its function.
Possible complications
If left untreated, arthritis of the hands and fingers will progress. The following complications are also possible:
- the development of a purulent inflammatory process with the transition to the tissues surrounding the joint, the development of abscesses, phlegmon and sepsis;
- fingertip necrosis, shortening and inflammation of soft tissues;
- subluxation and dislocation of small joints;
- various types of joint deformities;
- complete loss of function of the fingers and hands.
What to do with an exacerbation
With an exacerbation of arthritis, the joints become severely painful, the skin above them reddens, swells, finger movements become impossible due to pain. To reduce suffering it is necessary:
- give your hands a slightly raised position - this will reduce swelling;
- take any medicine from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen; will reduce pain and inflammation;
- apply to the skin over the diseased joint any external agents from the NSAID group - a gel or ointment; Diclofenac Emulgel helps a lot;
- see a doctor or call him at home.
With an exacerbation, it is impossible to delay a visit to the doctor, it is urgent to suppress the progression of the disease. It is impossible to do it yourself.
How arthritis of the fingers proceeds in the different clinical forms of the disease
Symptoms of arthritis of the hand and the nature of its course depend on the disease that led to its development. The defeat of the small joints of the hands is most often found in rheumatoid, psoriatic and gouty arthritis. But it can also occur in other clinical forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis
In most cases, arthritis begins slowly, imperceptibly. There are aching pains in the fingers. The nature of the pain is constant, aching, exhausting. In the morning after sleep, stiffness of movements appears, which can last up to 30 minutes or more.
After a while, the patient notices that the fingers began to swell in the joints. Most often, the overlying metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of the 2nd and 3rd toes are affected. The defeat is symmetrical on both arms. The pains of varying intensity are permanent. Over time, characteristic deformities of the spindle-shaped fingers appear.
Small painless subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules appear on the skin of the fingers and elbows. The course of the disease is slow, steadily progressing, accompanied by constant debilitating pain, deformity and loss of joint function.
Psoriatic arthritis
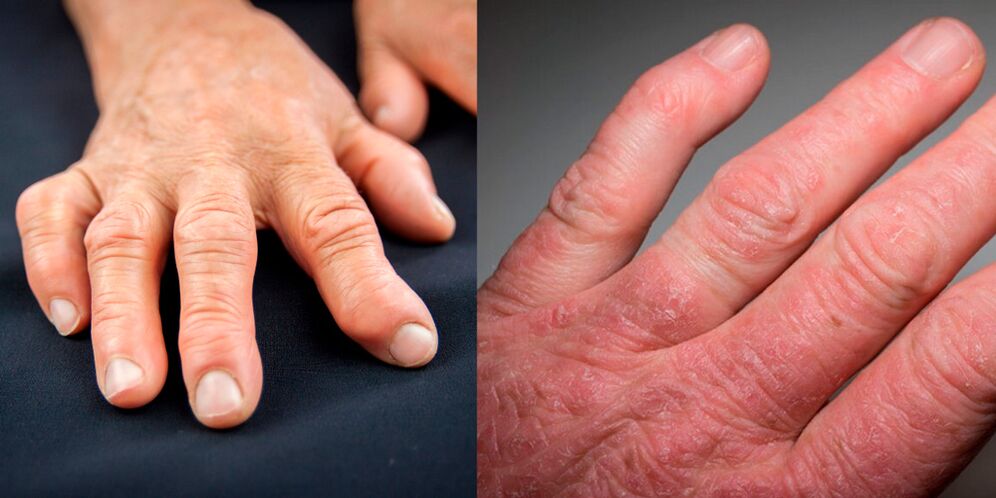
In this disease, arthritis develops in the distal (terminal) interphalangeal finger joints against the background of the already existing skin manifestations of psoriasis. But sometimes joint symptoms appear earlier or at the same time as skin symptoms. The disease in most cases begins acutely or subacutely with the appearance of redness, swelling and pain in the joints of the little fingers. The lesion is usually asymmetrical, while the fingers resemble sausages.
The disease proceeds with severe exacerbations and remissions. Almost always, the nails are involved in the pathological process. Over time, deformation of the fingertips occurs, they thicken, the nails become thinner and even deformed, a symptom of thimble appears - dotted indentations on the nail plates.
With a prolonged course of the disease, dislocations and subluxations of the small distal joints develop, as well as lysis (fusion) of the bones of the fingertips (X-ray sign) and shortening of the fingers.
Gouty arthritis
A gout attack begins acutely, with the appearance of severe pain, swelling and redness in the area of the affected joints. Small joints are often involved. Usually, the inflammation begins with the metacarpophalangeal joint of the 1st finger and then can spread to the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of the other fingers.
The pain is very severe, the attack can last from several hours to several weeks and then everything disappears. But with frequent attacks with damage to the joints themselves, their function is impaired.
Post-traumatic arthritis
This type of finger arthritis can develop against the background of an acute home, industrial or sports injury, proceed acutely with subsequent complete healing or (in the absence of the necessary assistance) be complicated by the addition of a purulent infection. Sometimes such an inflammatory process can turn into chronic, followed by deformation of the affected joints.
Initially, the chronic course of post-traumatic arthritis of the fingers assumes a constant minor imperceptible injury to the fingers. Most often this occurs in people of certain professions who perform small jobs. Arthritis develops slowly, the joints most traumatized during work are affected. If you do not change jobs, persistent deformation with dysfunction of the fingers develops.
Other types of arthritis
With such types of arthritis as reactive, infectious and idiopathic lesions of the small joints of the fingers are practically not found.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is established on the basis of the characteristic symptoms of the disease and is confirmed by the examination data:
- laboratory tests - reveal the presence of an inflammatory process, the presence or absence of infection, antibodies to infectious agents, rheumatoid factor;
- x-ray - reveals bone changes in the joints;
- Ultrasound - the presence of an increase in the volume of exudate in the joint cavity is a sign of an active inflammatory process;
- MRI - changes in joint and periarticular soft tissues.
Without additional methods of examination, it is impossible to establish the correct diagnosis (and, therefore, to prescribe adequate treatment). Therefore, if you experience pain in the small joints of your fingers, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Finger arthritis treatment
After establishing the final diagnosis, treatment of arthritis of the fingers is prescribed, which is carried out by a rheumatologist (sometimes in collaboration with other specialists - a surgeon, dermatovenerologist). It should be comprehensive, aimed at suppressing the progression of the pathological process and preventing violations of joint function. The complex treatment includes:
- pharmacological therapy;
- physiotherapy procedures;
- therapeutic gymnastics and massages;
- reflexology courses;
- folk remedies.
Pharmacological therapy
The first task of drug therapy is to alleviate the condition of a sick person. For this, drugs from the NSAID group are prescribed, which relieve pain, inflammation and swelling of tissues. Depending on the degree of activity of the inflammatory process, these drugs are prescribed in the form of injections (injections) or tablets for oral administration. Also, drugs of this group are prescribed externally in the form of gels, ointments and creams.
The most effective NSAID is Diclofenac, but it irritates the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, so it cannot be taken for a long time. Instead of Diclofenac, more modern drugs from the NSAID group are prescribed: Nimesulide, Celecoxib, etc. Such agents are used externally, Diclofenac ointment. The use of drugs from the NSAID group can bring significant relief to the patient.
Sometimes the inflammatory process is so pronounced that it is impossible to remove it with drugs from the NSAID group. In this case, glucocorticoid hormones are used: prednisolone, dexamethasone, etc. In the form of injections, inside in tablets or externally in the form of ointments. Intra-articular injection of hormones into small joints is rarely practiced.
To suppress autoimmune processes, drugs of the basic group are prescribed: methotrexate, sulfasalazine, leflunomide and biological agents (Rituximab). These drugs are selected by a rheumatologist and prescribed according to a special scheme for long courses.
To restore the function of the joints, chondroprotectors are prescribed, drugs that restore the cartilage tissue of the joints. They are also prescribed for long courses.
Means that improve blood circulation and metabolism in tissues: pentoxifylline and others help restore tissue trophism.
As fortifying agents, vitamins and minerals are prescribed that improve metabolism and help restore the general balance in the body.
Physiotherapy procedures
The complex treatment of arthritis of the fingers necessarily includes physiotherapy procedures. They, like drugs, are selected individually, depending on the clinical form and activity of the pathological process. This can be electrophoresis with hydrocortisone, UHF, laser or magnetotherapy, etc.
Massage and physical therapy
Courses of massage and remedial gymnastics are prescribed during the period when the inflammatory process subsides. They help improve blood circulation and metabolism in tissues, restore the function of small joints. At home, you can do the following physical exercises to improve mobility:
- roll a small elastic ball on the surface of the table with the surfaces of the fingers for a minute, actively involving the joints of the fingers involved in the process;
- with the fingertips of one hand touch the tip of the 1st finger of the opposite hand; start with the little finger and finish with the index; repeat the exercise 10 times;
- place your hands so that the tips of your fingers are slightly bent and touch the surface of the table; to bend each finger in turn and strike the table with it (like the keys of a piano);
- repeat three times.
Performing such exercises should be done daily, gradually increasing the number of approaches.
Folk remedies
How to treat arthritis of the fingers with folk remedies should be told by the doctor. He also chooses the most suitable technique. It is possible to use both herbal decoctions and infusions for oral administration, and external agents:
- a compress of kefir mixed with crushed gypsum at the rate of 50 g of gypsum for 75 - 100 ml of kefir; you should get a thick mixture, which must be applied once a day at night; for this, it must be applied to a napkin made of cotton material, applied to a sore spot, on top - polyethylene and insulation; then leave it all night; perfectly relieves swelling and pain;
- infusion of celery roots; Put 20 g of crushed raw materials (dry or fresh) in a thermos overnight, pour 200 ml of boiling water; the next day, drink 3 - 4 servings before meals; the course of treatment is 2 weeks; relieves pain and swelling well.
Surgery
This type of small joint arthritis treatment is rarely used. With pronounced, not amenable to conservative treatment, arthritis is sometimes performed synovectomy - removal of a part of the synovial membrane that produces a large volume of exudate.
In some cases, the joint is replaced with an artificial one, but this is a rather rare operation.
The current strategy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in this article.
Clinical Approach to Finger Arthritis
In our clinic, the patient is carefully examined using the latest laboratory and instrumental methods, including MRI, and only after that a treatment is prescribed, which is selected individually for each patient.
A feature of the treatment in our clinic is that complex therapy includes:
- modern Western methods of treatment to eliminate the main manifestations of arthritis of the fingers;
- traditional oriental methods of treating diseases, which allow you to restore balance in the body, establish the relationship of all organs and systems; this leads to the elimination of inflammation, swelling and pain in the joints and suppression of the progression of the disease.
The combination of Western and Eastern techniques allows us to quickly and painlessly relieve our patients from pain and thus effectively restore the function of damaged joints. The clinic's specialists have extensive experience in treating arthritis of the fingers. You can find out more about the treatment methods in our clinic on our website.
General clinical guidelines
Patients with finger arthritis are advised to:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, temperament; heal in time, eliminate all foci of infection, which can become a trigger in the development of exacerbations of arthritis;
- get rid of bad habits, eat right, regulate sleep and wakefulness;
- in case of exacerbation of arthritis, do not load your fingers, do not do housework, including washing dishes;
- during remission at home, do physical exercises for the hands; classes should be held daily;
- completely abandon self-medication and adhere to the doctor's recommendations in everything.
Prevention of arthritis of the fingers
The prevention of arthritis is especially important for people with a genetic predisposition to this disease (close relatives with this pathology). To maintain health, they must adhere to the following recommendations:
- you can not load your hands with long-term heavy or painstaking physical labor, even at home;
- hypothermia must be avoided, hands must be avoided;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, temper;
- play feasible sports, train every day;
- avoid prolonged stress.
Diet
Special nutrition is needed only for gouty arthritis of the fingers. The diet of such patients should not contain strong broths, offal, meat of young animals, alcohol, sorrel, salad, strong tea, coffee, chocolate.

In other cases, it is enough to adhere to the principles of a healthy diet: eat lean meat and dairy products, fish (fatty sea fish is useful), cereals, cereals, vegetables, fruits. Avoid high calorie foods, sweets, muffins, hot spices, fried and smoked foods. Meals should be regular.
Finger arthritis often develops unnoticed. It is very important to pay attention to aching pains in the fingers in time and to consult a doctor in a timely manner. But even if you've wasted your time and there are clear signs of arthritis, don't despair - you can help at any time. It is problematic to completely cure a chronic disease, but it is quite possible to stop its progression, relieve pain and improve the quality of life.
























